Introduction:
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the global economy, leading to unprecedented challenges for businesses across various industries. One area that has been particularly affected is the real estate sector, where lenders have had to reassess their underwriting criteria and risk management strategies. This article explores the impact of EBITDAR adjustments and COVID rent add-backs on lender acceptance rates, highlighting the evolving landscape of real estate lending.

I. Understanding EBITDAR Adjustments:
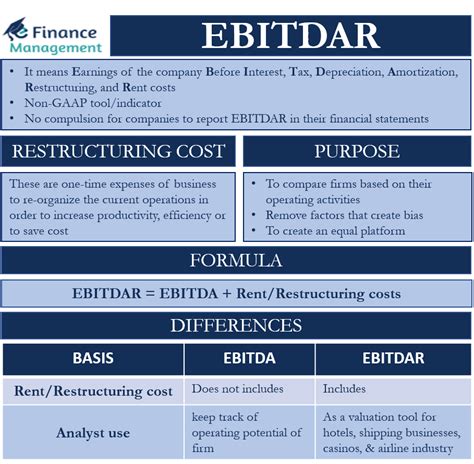
EBITDAR stands for Earnings Before Interest, Tax, Depreciation, Amortization, and Rent. It is a financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of a business. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many real estate investors faced challenges in maintaining rental income, leading to adjustments in EBITDAR calculations. These adjustments aim to provide a more accurate representation of a property’s cash flow and its ability to generate income.
II. COVID Rent Add-Backs:
In response to the pandemic’s impact on rental income, lenders have started to incorporate COVID rent add-backs into their underwriting process. A COVID rent add-back is an adjustment that restores the projected rental income to pre-pandemic levels. This adjustment is made to recognize the potential recovery of rental income as the economy begins to reopen.
III. Lender Acceptance Rates:
The integration of EBITDAR adjustments and COVID rent add-backs has had a notable impact on lender acceptance rates. The following points highlight the key aspects of this impact:
A. Enhanced Underwriting Criteria:
Lenders have become more flexible in their underwriting criteria, allowing for EBITDAR adjustments and COVID rent add-backs. This flexibility aims to support real estate investors facing short-term rental income challenges due to the pandemic.
B. Increased Acceptance Rates:
As a result of these adjustments, lender acceptance rates for real estate loans have improved. Properties that may have been considered risky before the pandemic are now more likely to be approved, provided that they meet the revised underwriting criteria.
C. Improved Risk Management:
The inclusion of EBITDAR adjustments and COVID rent add-backs in lender underwriting processes has enhanced risk management. Lenders can better assess the potential impact of the pandemic on a property’s cash flow and adjust their lending strategies accordingly.
IV. Challenges and Considerations:
While EBITDAR adjustments and COVID rent add-backs have improved lender acceptance rates, there are still challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
A. Temporary Adjustments:
These adjustments are designed to be temporary and are intended to reflect the short-term impact of the pandemic. Lenders may revert to more conservative underwriting criteria once the economy stabilizes.
B. Property-Specific Factors:
The effectiveness of EBITDAR adjustments and COVID rent add-backs may vary depending on the property’s location, tenant mix, and other specific factors. Lenders must carefully evaluate these factors when considering loan approvals.
Conclusion:
The integration of EBITDAR adjustments and COVID rent add-backs has had a positive impact on lender acceptance rates in the real estate sector. As the economy continues to recover from the pandemic, these adjustments will play a crucial role in supporting real estate investors and ensuring the stability of the real estate market. However, lenders must remain vigilant and continue to monitor the evolving landscape to mitigate potential risks.