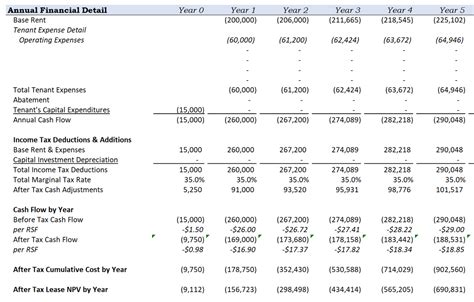
Title: Lease Mileage Overages: Cost Analysis of 10k Miles vs 15k Annual Limit
Introduction:

When leasing a vehicle, one of the critical factors to consider is the mileage limit. Most lease agreements include a set number of miles that can be driven annually, beyond which the lessee may incur additional costs. This article provides a cost analysis of lease mileage overages at two common limits: 10,000 miles and 15,000 miles. By understanding the potential costs, lessees can make an informed decision when selecting their mileage limit.
10,000 Mile Annual Limit:
Lease agreements with a 10,000-mile annual limit are often more affordable than those with a 15,000-mile limit. However, this also means that lessees have a stricter mileage cap, requiring them to be more mindful of their driving habits.
1. Initial Cost:
A lease with a 10,000-mile limit may have a lower monthly payment compared to a 15,000-mile lease. This is because the lease company incurs fewer costs when anticipating a lower mileage.
2. Mileage Overage Costs:
If a lessee exceeds the 10,000-mile limit, they will incur additional costs. The overage fee is usually calculated based on a per-mile rate, which can vary depending on the vehicle and lease terms. For instance, if the overage rate is $0.25 per mile, exceeding the limit by 500 miles would result in a $125 fee.
3. Potential for Higher Costs:
Since the mileage cap is lower, lessees who exceed the limit may incur higher costs over the lease term. This is especially true if they consistently exceed the limit by a significant amount.
15,000 Mile Annual Limit:
Lease agreements with a 15,000-mile annual limit offer more flexibility for lessees who expect to drive more than 10,000 miles annually.
1. Initial Cost:
A lease with a 15,000-mile limit may have a higher monthly payment compared to a 10,000-mile lease. This is due to the increased risk and potential costs associated with higher mileage.
2. Mileage Overage Costs:
Similar to the 10,000-mile limit, exceeding the 15,000-mile limit will result in additional costs. The overage fee per mile may be slightly lower compared to the 10,000-mile limit, but the total cost can still be significant if the lessee exceeds the limit by a large margin.
3. Potential for Higher Costs:
While the 15,000-mile limit provides more flexibility, lessees should still be cautious about exceeding the mileage. The higher initial cost and potential for higher overage fees make it important to consider their driving habits when selecting this limit.
Conclusion:
The choice between a 10,000-mile and 15,000-mile annual mileage limit for a lease depends on the lessee’s driving habits and preferences. While a 10,000-mile limit may result in lower monthly payments, it requires stricter adherence to mileage limits. On the other hand, a 15,000-mile limit offers more flexibility but comes with a higher initial cost and potential for higher overage fees. By understanding the potential costs associated with each limit, lessees can make an informed decision that aligns with their driving needs.