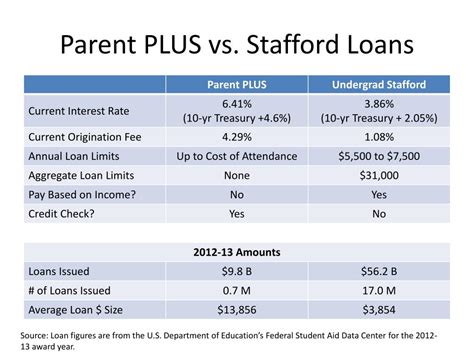
Introduction:
As parents, supporting our children’s education is often a top priority. However, the rising costs of higher education can lead to financial strain and the need for student loans. When it comes to securing a student loan, there are two popular options: co-signed loans and Parent PLUS loans. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison between these two options, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages to help parents make an informed decision.

1. Co-Signed Loans:
a. Definition:
A co-signed loan is a type of student loan where a creditworthy individual (usually a parent) agrees to assume responsibility for the loan if the borrower fails to repay the debt.
b. Eligibility:
To co-sign a loan, the co-signer must meet certain criteria, such as having a good credit score and a stable income.
c. Repayment:
If the borrower defaults on the loan, the co-signer becomes liable for the remaining balance. This means that the co-signer’s credit score and financial stability can be negatively affected.
d. Benefits:
– Lower interest rates: Co-signed loans often come with lower interest rates than Parent PLUS loans, which can save the borrower money in the long run.
– Easier approval process: With a co-signer, the borrower may have a better chance of qualifying for the loan, especially if they have limited credit history.
e. Disadvantages:
– Shared responsibility: The co-signer is equally responsible for the loan, which can lead to financial strain and potential damage to their credit score if the borrower defaults.
– Limited control: The co-signer has no control over the loan’s repayment terms or the borrower’s usage of the funds.
2. Parent PLUS Loans:
a. Definition:
A Parent PLUS loan is a federal student loan that allows parents to borrow money on behalf of their dependent children to help pay for education expenses.
b. Eligibility:
Parents must have a good credit history to qualify for a Parent PLUS loan. If they have an adverse credit history, they may need an endorser or an eligible co-signer.
c. Repayment:
The parent who takes out the Parent PLUS loan is solely responsible for repaying the debt, regardless of the student’s financial situation.
d. Benefits:
– Higher loan limits: Parent PLUS loans often have higher borrowing limits compared to co-signed loans, making them more suitable for students with higher education costs.
– Flexible repayment options: Parents have various repayment plans and options, including income-driven repayment, which can be beneficial for those with financial constraints.
e. Disadvantages:
– Higher interest rates: Parent PLUS loans typically have higher interest rates compared to co-signed loans, which can result in higher overall costs.
– Borrower’s financial liability: While the parent is solely responsible for repayment, the student may still be required to contribute to the loan through work-study or other financial aid options.
Conclusion:
When it comes to choosing between co-signed loans and Parent PLUS loans, there are several factors to consider. Co-signed loans offer lower interest rates and a better chance of loan approval, but they come with shared responsibility and potential damage to the co-signer’s credit score. Parent PLUS loans provide higher borrowing limits and flexible repayment options but often come with higher interest rates. Ultimately, the best option depends on the borrower’s financial situation, the co-signer’s willingness to take on the responsibility, and the specific needs of the student. Consulting with a financial advisor can help parents make a well-informed decision that aligns with their goals and values.