In the world of factoring, where businesses sell their accounts receivable to a third-party in exchange for immediate cash, fraud prevention is paramount. One crucial aspect of this prevention is cross-checking accounts receivable aging. This process ensures that the receivables being factored are legitimate and reduces the risk of fraud. In this article, we will explore the importance of cross-checking accounts receivable aging in factoring fraud prevention.
**Understanding Accounts Receivable Aging**

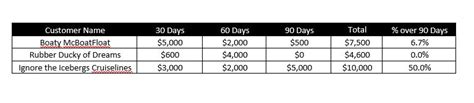
Accounts receivable aging is a financial metric that categorizes a company’s receivables based on the time elapsed since the sale was made. It is typically divided into four categories: current, 30 days past due, 60 days past due, and 90 days past due or more. By monitoring the aging of accounts receivable, businesses can identify potential issues, such as late payments or non-payments, and take appropriate actions.
**The Role of Cross-Checking in Fraud Prevention**
Cross-checking accounts receivable aging is a vital step in preventing fraud within the factoring process. Here’s how it helps:
1. **Verification of Sales**: By cross-checking the aging of accounts receivable, factoring companies can verify that the sales reported by the business are legitimate. This helps ensure that the receivables being factored are indeed owed to the business.
2. **Early Detection of Issues**: Cross-checking allows factoring companies to identify discrepancies or anomalies in the aging of accounts receivable. For example, if a particular customer’s account is suddenly showing a high number of past-due receivables, it may indicate a potential issue, such as fraud or a billing error.
3. **Reduced Risk of Fraud**: By closely monitoring the aging of accounts receivable, factoring companies can reduce the risk of fraud. This is because they can quickly identify and address any suspicious activity, such as duplicate invoices or payments to non-existent customers.
4. **Enhanced Due Diligence**: Cross-checking accounts receivable aging is an essential part of due diligence for factoring companies. It helps them assess the creditworthiness of the business and the likelihood of default on the receivables.
**Best Practices for Cross-Checking Accounts Receivable Aging**
To effectively cross-check accounts receivable aging and prevent fraud, factoring companies should consider the following best practices:
1. **Regular Audits**: Conduct regular audits of the aging of accounts receivable to identify any discrepancies or potential issues.
2. **Collaboration with the Business**: Work closely with the business to verify the accuracy of the accounts receivable aging and ensure that the reported sales are legitimate.
3. **Use of Technology**: Implementing advanced technology, such as accounting software and data analytics tools, can help streamline the cross-checking process and improve accuracy.
4. **Training Employees**: Ensure that employees responsible for cross-checking accounts receivable aging are well-trained in identifying potential fraud indicators.
In conclusion, cross-checking accounts receivable aging is a critical component of fraud prevention in the factoring industry. By verifying the legitimacy of receivables and identifying potential issues early on, factoring companies can protect themselves and their clients from the risks associated with fraud.