Introduction:
The landscape of student loan refinancing has been rapidly evolving, and with it, the risks associated with private loan refinancing have become a topic of concern. As federal borrower protections are being scaled back, borrowers must navigate the complexities of refinancing their private student loans with greater caution. This article aims to analyze the traps that borrowers may encounter when refinancing their private loans, especially in the absence of robust federal borrower protections.

I. The Shift in Federal Borrower Protections
A. The Evolution of Federal Student Loan Protections
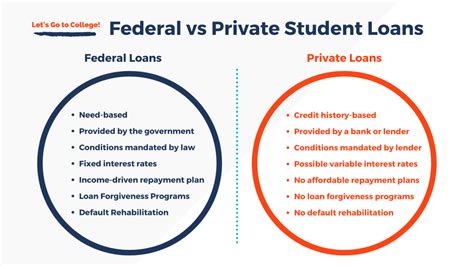
Historically, federal student loans have been accompanied by several borrower protections, including income-driven repayment plans, loan forgiveness programs, and federal bankruptcy protections. However, recent changes have led to a reduction in these protections for borrowers with private student loans.
B. The Role of the CFPB
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) has played a crucial role in advocating for borrowers’ rights and enforcing federal borrower protections. However, budget cuts and policy changes have limited the CFPB’s ability to oversee the private loan refinancing market.
II. The Traps of Private Loan Refinancing
A. Hidden Fees and Costs
Private loan refinancing companies may charge various fees and costs, such as origination fees, prepayment penalties, and late fees. Borrowers need to be vigilant and understand the total cost of refinancing their loans before proceeding.
B. Loss of Federal Borrower Protections
Refinancing a private student loan means losing the federal borrower protections mentioned earlier. Borrowers must weigh the benefits of refinancing against the potential risks associated with private loans, such as the inability to participate in income-driven repayment plans or loan forgiveness programs.
C. Less Flexibility in Repayment Options
Private loans often have stricter repayment terms and fewer options compared to federal loans. Borrowers may find themselves with limited flexibility in managing their debt, which can lead to financial stress and difficulty in maintaining a healthy credit score.
III. Strategies for Navigating Private Loan Refinancing
A. Research and Comparison Shopping
Borrowers should thoroughly research and compare different refinancing options to find the best rates and terms. This includes checking for hidden fees, loan forgiveness opportunities, and customer reviews.
B. Consult with Financial Advisors
Seeking advice from financial advisors or credit counselors can help borrowers make informed decisions and avoid potential pitfalls.
C. Maintain Good Credit Practices
Borrowers should focus on maintaining good credit practices, such as paying bills on time and keeping their debt-to-income ratio low, even after refinancing.
Conclusion:
As federal borrower protections wane, borrowers must be aware of the potential traps associated with private loan refinancing. By conducting thorough research, seeking professional advice, and maintaining good credit practices, borrowers can navigate the refinancing process more effectively and minimize the risks involved.