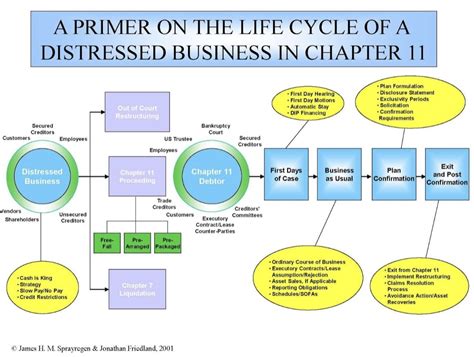
In the complex world of business finance, distressed companies often find themselves at a crossroads, facing the daunting prospect of bankruptcy. Chapter 11 bankruptcy, a reorganization process under the United States Bankruptcy Code, provides these companies with a chance to restructure their debts and continue operations. One of the key strategies employed during this period is the loan-to-own financing approach. This article delves into the intricacies of distressed business financing loan-to-own strategies in Chapter 11.
**Understanding Chapter 11 Bankruptcy**

Chapter 11 bankruptcy is a legal process that allows businesses to continue operating while they restructure their debts. It is designed to provide companies with a fresh start, enabling them to pay off creditors over time, often at a reduced amount. During this period, the business may seek financing to help it through the restructuring process.
**The Loan-to-Own Strategy**
The loan-to-own strategy is a financing arrangement where a lender provides a loan to a distressed business with the understanding that the lender will eventually acquire ownership of the business. This approach is particularly attractive to lenders because it offers the potential for higher returns, as well as a direct stake in the business’s future success.
**Key Aspects of Loan-to-Own Strategies in Chapter 11**
1. **Initial Loan Terms**: The initial loan is typically structured to provide the business with the necessary capital to continue operations and restructure its debts. The terms of the loan, including interest rates and repayment schedules, are negotiated between the borrower and the lender.
2. **Ownership Transition**: Once the business has successfully restructured its debts and improved its financial position, the lender may exercise the option to acquire ownership. This transition is often subject to certain conditions, such as the business achieving specific financial milestones or the approval of the bankruptcy court.
3. **Risk Mitigation**: Lenders employing the loan-to-own strategy often seek to mitigate their risks by requiring the business to provide collateral or personal guarantees. These measures help ensure that the lender can recover its investment in the event that the business fails to meet its obligations.
4. **Legal and Regulatory Considerations**: The loan-to-own strategy must comply with various legal and regulatory requirements, including those governing bankruptcy proceedings. This includes obtaining approval from the bankruptcy court and ensuring that the transaction is in the best interests of creditors.
**Advantages of Loan-to-Own Strategies**
1. **Access to Capital**: Distressed businesses may find it challenging to secure traditional financing. The loan-to-own strategy provides an alternative source of capital, allowing the business to continue operations and restructure its debts.
2. **Potential for Higher Returns**: Lenders may be willing to provide financing at more favorable terms, knowing that they stand to gain ownership of the business and potentially benefit from its future success.
3. **Enhanced Control**: By acquiring ownership, lenders can play a more active role in the business’s operations, helping to ensure its long-term viability.
**Conclusion**
Distressed business financing loan-to-own strategies in Chapter 11 bankruptcy offer a unique approach to helping struggling companies survive and thrive. While these strategies come with their own set of risks and complexities, they provide a valuable tool for lenders and businesses alike. As the business landscape continues to evolve, the loan-to-own strategy is likely to remain an important component of the financial toolkit available to distressed companies and their creditors.