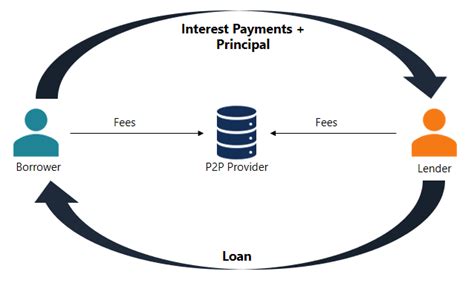
In the ever-evolving landscape of financial services, peer-to-peer (P2P) lending has emerged as a popular alternative to traditional banking. This innovative model connects borrowers directly with lenders, cutting out the middleman and potentially offering more favorable interest rates. However, with this convenience comes a set of risks, particularly when it comes to unsecured personal loans. This article delves into the issue of default rates in the P2P lending sector, specifically highlighting the 12% default rate for unsecured personal loans.
The allure of P2P lending lies in its ability to provide borrowers with quick access to funds without the stringent requirements often associated with traditional banks. However, this ease of access also makes borrowers more susceptible to defaulting on their loans. The 12% default rate for unsecured personal loans in the P2P lending industry is a significant concern for both borrowers and lenders alike.

One of the primary reasons for the high default rate is the lack of collateral. Unlike secured loans, where borrowers put up assets such as property or vehicles as collateral, unsecured personal loans do not require any such guarantees. This makes it easier for borrowers to obtain the funds they need, but it also leaves them more vulnerable to financial hardship, which can lead to default.
Another contributing factor to the high default rate is the rapid growth of the P2P lending industry. As the market expands, more borrowers are entering the fray, many of whom may not have a solid credit history or the financial stability to repay their loans. This influx of borrowers with varying creditworthiness has inevitably led to an increase in default rates.
Moreover, the P2P lending model often relies on algorithms to match borrowers with lenders, which can sometimes result in mismatches. Lenders may not always have access to comprehensive information about the borrowers, which can lead to poor risk assessment and, ultimately, higher default rates.
Despite these challenges, the P2P lending industry is not without its benefits. For borrowers, the competitive interest rates and faster loan approval process can be a godsend. For lenders, the potential for higher returns on investment can be enticing. However, it is crucial for both parties to be aware of the risks involved and take appropriate measures to mitigate them.
Here are some strategies to reduce the default rate in unsecured personal loans within the P2P lending sector:
1. Enhanced credit screening: Implementing a more rigorous credit screening process can help identify borrowers with a higher likelihood of defaulting.
2. Diversification: By spreading their investments across a wide range of borrowers, lenders can reduce their exposure to default risk.
3. Education: Educating borrowers on the responsibilities and consequences of taking out a loan can help prevent defaults.
4. Loan terms and conditions: Offering flexible loan terms and conditions can make it easier for borrowers to repay their loans, thus reducing the default rate.
In conclusion, the 12% default rate for unsecured personal loans in the P2P lending industry is a concerning issue. However, by implementing the aforementioned strategies and remaining vigilant about the risks involved, both borrowers and lenders can work together to create a more stable and profitable P2P lending ecosystem.