Title: Auto Loan Default: The Impact of 60-Day Delinquency Repossession Timelines
Introduction:

The auto loan industry has witnessed a significant rise in defaults over the past few years. One of the critical factors contributing to this trend is the 60-day delinquency repossession timelines. This article delves into the implications of these timelines on both lenders and borrowers, highlighting the challenges and potential solutions.
I. Understanding Auto Loan Defaults
1. Definition: An auto loan default occurs when a borrower fails to make payments on their auto loan, leading to the lender taking possession of the vehicle.
2. Causes: Factors such as financial hardship, job loss, or unexpected expenses can contribute to auto loan defaults.
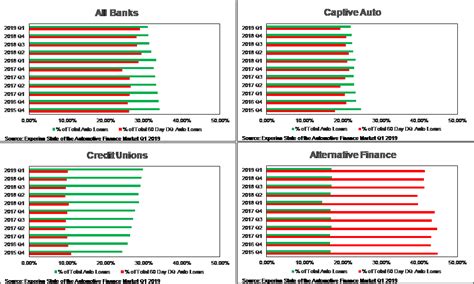
II. The Role of 60-Day Delinquency Repossession Timelines
1. Purpose: These timelines are designed to give borrowers a grace period before the lender initiates repossession proceedings.
2. Standard: Most lenders have a 60-day delinquency period, but this can vary depending on the specific terms of the loan agreement.
III. Implications for Lenders
1. Financial Loss: Repossession can result in financial losses for lenders, as they may have to sell the vehicle at a lower price than the outstanding loan balance.
2. Legal Costs: Initiating repossession proceedings can be costly, including hiring repossession agencies and pursuing legal action if necessary.
3. Risk Management: Lenders must balance the risk of default with the potential for financial loss, often leading to stricter lending criteria.
IV. Implications for Borrowers
1. Credit Score Impact: Auto loan defaults can significantly damage a borrower’s credit score, making it difficult to secure future credit.
2. Legal Consequences: Borrowers may face legal action from lenders, including wage garnishment or liens on other assets.
3. Emotional Stress: The repossession of a vehicle can lead to emotional distress and a loss of transportation, impacting daily life.
V. Challenges and Solutions
1. Communication: Lenders and borrowers should maintain open communication to address financial difficulties and explore repayment options.
2. Loan Modifications: Lenders may consider modifying the loan terms, such as extending the repayment period or reducing the interest rate, to help borrowers stay current on their payments.
3. Alternative Repayment Plans: Some lenders may offer alternative repayment plans, such as interest-only payments or deferred payments, to help borrowers manage their debt.
4. Financial Education: Borrowers should be educated on responsible borrowing and budgeting to prevent defaults in the future.
Conclusion:
The 60-day delinquency repossession timelines have become a crucial factor in the auto loan industry. While they provide a grace period for borrowers, they also pose challenges for lenders. By implementing effective communication, loan modifications, and financial education, both parties can work together to mitigate the risks associated with auto loan defaults.