Introduction:
The automotive industry has seen a significant growth in the financing of vehicles, with subprime auto loans playing a crucial role. However, the high-interest rates, particularly the 20% APR, and the increasing risk associated with repo (repurchase) probability models have raised concerns among lenders and borrowers alike. In this article, we will discuss the challenges posed by these factors and the potential impact on the automotive market.

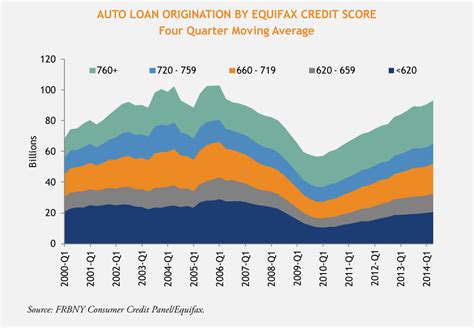
1. The Subprime Auto Market:
Subprime auto loans are tailored for borrowers with lower credit scores, who may face higher interest rates and stricter loan terms. These loans have become increasingly popular as car manufacturers and dealerships seek to boost sales and attract a wider customer base. However, this growth has also brought about a rise in defaults and repossession rates.
2. The 20% APR Challenge:
A 20% annual percentage rate (APR) is considered a high-interest rate, particularly for subprime borrowers. Such rates can lead to increased financial strain, higher defaults, and a negative impact on the overall automotive market. Lenders may face increased credit risk, while borrowers may struggle to manage their loan obligations.
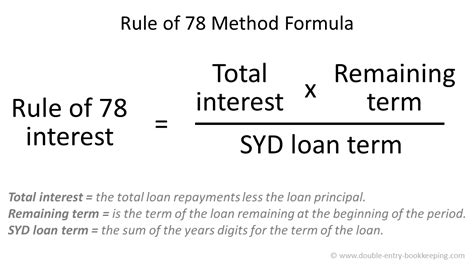
3. Repo Risk Probability Models:
Repo risk probability models are tools used by lenders to assess the likelihood of a borrower defaulting on their loan, leading to repossession. These models rely on various factors, including credit scores, income, and payment history. However, the accuracy of these models can be questioned, particularly in the subprime auto loan market.
4. The Impact on the Automotive Market:
The combination of high-interest rates and repo risk probability models can have a profound impact on the automotive market. Here are some potential consequences:
a. Reduced Vehicle Sales: High-interest rates can deter potential buyers, leading to a decrease in vehicle sales.
b. Increased Defaults: Borrowers struggling with high-interest payments may default on their loans, leading to an increase in repossession rates.
c. Financial Strain on Lenders: Lenders facing higher defaults and increased repo risk may find it challenging to maintain profitability.
d. Market Instability: The subprime auto loan market’s instability can have a ripple effect on the overall automotive industry.
5. Potential Solutions:
To mitigate the risks associated with subprime auto loans, lenders and manufacturers can consider the following strategies:
a. Improved Credit Scoring Models: Developing more accurate credit scoring models can help lenders better assess the risk associated with each borrower.
b. Flexible Loan Terms: Offering more flexible loan terms, such as lower interest rates and longer repayment periods, can make loans more affordable for borrowers.
c. Enhanced Education: Educating borrowers on the importance of responsible borrowing and loan management can help reduce defaults.
d. Regulatory Oversight: Strengthening regulatory oversight can ensure that lenders adhere to ethical lending practices and protect borrowers from predatory lending.
Conclusion:
The subprime auto loan market’s challenges, including the 20% APR and repo risk probability models, are not to be taken lightly. By implementing strategies to mitigate these risks, lenders, manufacturers, and regulators can work together to create a more stable and sustainable automotive market.