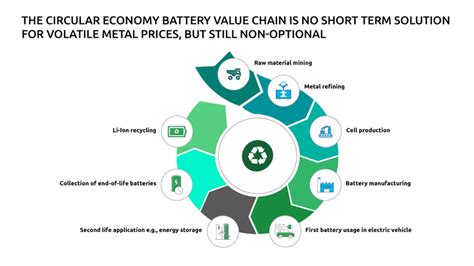
Introduction:
The rise in popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) has brought about a new set of challenges and considerations for both manufacturers and consumers. One such challenge is the issue of battery depreciation, which can significantly affect the residual value of EVs and, in turn, the cost of leasing these vehicles. This article delves into the impact of a 30% residual value on EV leases and explores potential solutions to mitigate this issue.

1. Understanding Battery Depreciation:
Battery depreciation refers to the decrease in the value of an EV’s battery over time due to various factors, such as wear and tear, aging, and technological advancements. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, EV batteries are the primary source of power and have a limited lifespan. This depreciation can lead to a significant reduction in the vehicle’s resale value and, consequently, the cost of leasing.
2. The 30% Residual Value Impact:
The 30% residual value is a common benchmark used to determine the lease price of an EV. This value represents the expected value of the vehicle at the end of the lease term, usually three to four years. A 30% residual value implies that the battery will have depreciated by 70% over the same period.
The impact of a 30% residual value on EV leases can be substantial:
a. Higher Monthly Payments: To compensate for the 70% depreciation, leasing companies may charge higher monthly payments, making the lease more expensive for consumers.
b. Limited Vehicle Choice: With higher lease costs, consumers may have limited options when selecting an EV, as some vehicles may not be financially viable under the 30% residual value scenario.
c. Reduced Market Value: A 30% residual value can also affect the market value of EVs, making it more challenging for consumers to sell their leased vehicles after the lease term.
3. Mitigating the Impact:
To address the 30% residual value impact on EV leases, several solutions can be considered:
a. Battery Health Monitoring: Implementing advanced battery health monitoring systems can help predict the remaining lifespan of the battery, allowing leasing companies to offer more accurate residual values and, consequently, lower lease costs.
b. Battery Replacement Programs: Leasing companies can offer battery replacement programs, allowing consumers to replace the battery after the lease term at a reduced cost. This can help maintain the vehicle’s value and reduce the impact of battery depreciation.
c. Innovative Leasing Models: Exploring innovative leasing models, such as flat-rate leases, can help mitigate the impact of battery depreciation. This model would involve a fixed monthly payment, regardless of the vehicle’s residual value.
Conclusion:
The 30% residual value impact on EV leases is a significant concern for both manufacturers and consumers. By understanding the factors contributing to battery depreciation and implementing strategies to mitigate its impact, leasing companies can offer more affordable and attractive EV leasing options. As the EV market continues to grow, addressing these challenges will be crucial in ensuring the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.