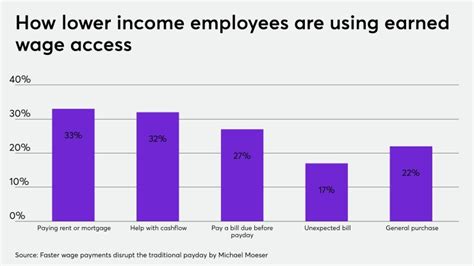
In today’s fast-paced world, the need for immediate access to earned wages has become more pressing than ever. Paycheck advances have emerged as a popular solution, offering employees the convenience of receiving a portion of their earned wages before their regular pay date. However, there are two primary options when it comes to paycheck advances: employer-based 0% advances and earned wage access (EWA) fees. This article aims to shed light on the differences between these two options and help you make an informed decision.
**Employer-Based 0% Advances**

Employer-based 0% advances, as the name suggests, are provided by the employer without any additional fees or interest. These advances are typically given to employees who have a good standing with their employer and demonstrate financial need. Here are some key points to consider:
1. **No Fees or Interest**: This is the most attractive feature of employer-based 0% advances. Employees can receive the advance without worrying about additional costs.
2. **Easy Application Process**: The application process is usually straightforward and can be completed within a short period. Employees can apply for an advance through their employer’s HR department or an online portal.
3. **Eligibility Criteria**: Eligibility for these advances is often based on the employee’s tenure with the company and their financial situation. Employers may require proof of financial need, such as bank statements or other financial documents.
4. **Payment Terms**: The repayment terms are usually flexible and may vary depending on the employer’s policy. Some employers may require the advance to be repaid from the next paycheck, while others may offer longer repayment periods.
**Earned Wage Access Fees**
Earned wage access (EWA) is a newer concept that allows employees to access their earned wages before their regular pay date, typically through a third-party service. While EWA fees can vary, here are some factors to consider:
1. **Fees and Interest**: EWA services often charge a fee or interest for accessing earned wages. These fees can vary based on the amount of money accessed and the duration of the advance.
2. **Application Process**: Applying for an EWA advance is generally easy and can be done through a mobile app or online platform. Employees can request an advance at any time and receive the funds within a few hours or days.
3. **Eligibility Criteria**: Eligibility for EWA services may vary by provider. Some services require a minimum number of hours worked or a minimum pay threshold, while others have more flexible requirements.
4. **Payment Terms**: EWA services typically offer repayment options that align with the employee’s next pay date. However, it’s important to read the fine print to understand any potential fees or interest that may apply.
**Conclusion**
Both employer-based 0% advances and earned wage access fees offer employees the convenience of accessing earned wages before their regular pay date. However, the key difference lies in the fees and interest associated with each option. Employer-based 0% advances are ideal for employees who want to avoid additional costs, while EWA fees may be a viable alternative for those who need immediate access to their wages and are willing to pay a fee for the convenience.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on the individual’s financial situation and priorities. It’s important to weigh the pros and cons of each option before deciding which one is right for you.