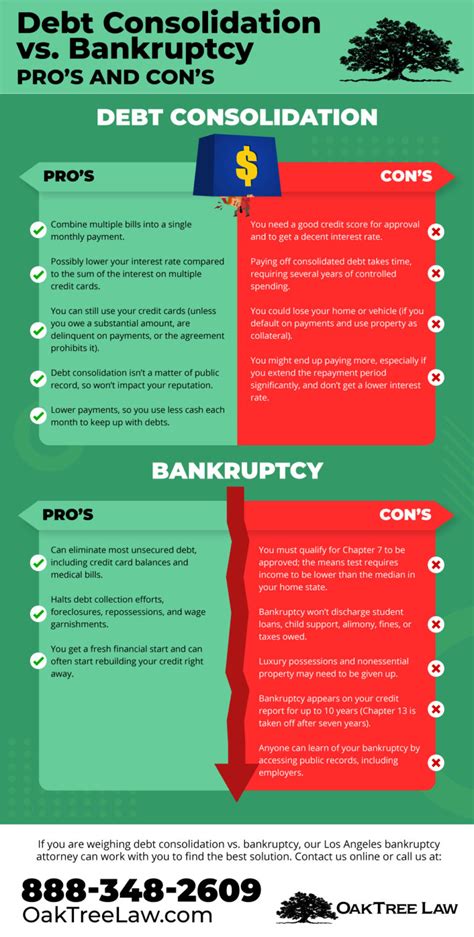
Introduction:
When faced with overwhelming debt, individuals often consider two potential solutions: debt settlement and bankruptcy. Both options can have a significant impact on one’s credit report, but the extent of damage can vary. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison between debt settlement and bankruptcy, focusing on the credit report damage each option entails within a 7-year period.

Debt Settlement:
Debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to pay off a portion of the total debt in exchange for a lump sum payment. This process can be beneficial for those who cannot afford their current debt obligations. However, it comes with certain drawbacks, particularly when it comes to credit report damage.
1. Settlements typically appear as “settled” or “paid as agreed” on credit reports, which may lower credit scores compared to paying off debts in full.
2. The settlement may be reported as a negative item on credit reports for up to 7 years.
3. Credit scores can be negatively impacted by the late payments and collection accounts that led to the need for debt settlement.
4. While the settlement itself is reported for 7 years, the underlying debt may remain on the credit report for up to 7 years after the account is closed.
Bankruptcy:
Bankruptcy is a legal process that allows individuals to eliminate or restructure their debts. There are two main types of bankruptcy: Chapter 7 and Chapter 13. Both options have varying degrees of credit report damage, particularly within a 7-year period.
1. Chapter 7 bankruptcy: This type of bankruptcy involves liquidating assets to pay off creditors and discharge remaining debts. It is reported on credit reports for 7 years from the filing date.
2. Chapter 13 bankruptcy: This type of bankruptcy allows individuals to repay a portion of their debts over a 3-5-year period. It is reported on credit reports for 7 years from the filing date.
3. Both Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy can significantly lower credit scores, but they may not be reported for the entire 7-year period.
4. Once bankruptcy is discharged, the negative impact on credit scores tends to diminish over time.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, both debt settlement and bankruptcy have their own pros and cons, particularly when it comes to credit report damage. Debt settlement may result in a shorter negative mark on credit reports (up to 7 years), but it does not eliminate the underlying debt. On the other hand, bankruptcy can provide a fresh start but is reported for a longer period and has a more substantial impact on credit scores.
Ultimately, individuals must weigh the short-term benefits of debt settlement against the long-term consequences of bankruptcy when making a decision that aligns with their financial goals and situation. Consulting with a financial advisor or bankruptcy attorney can provide personalized guidance to help individuals choose the best course of action.